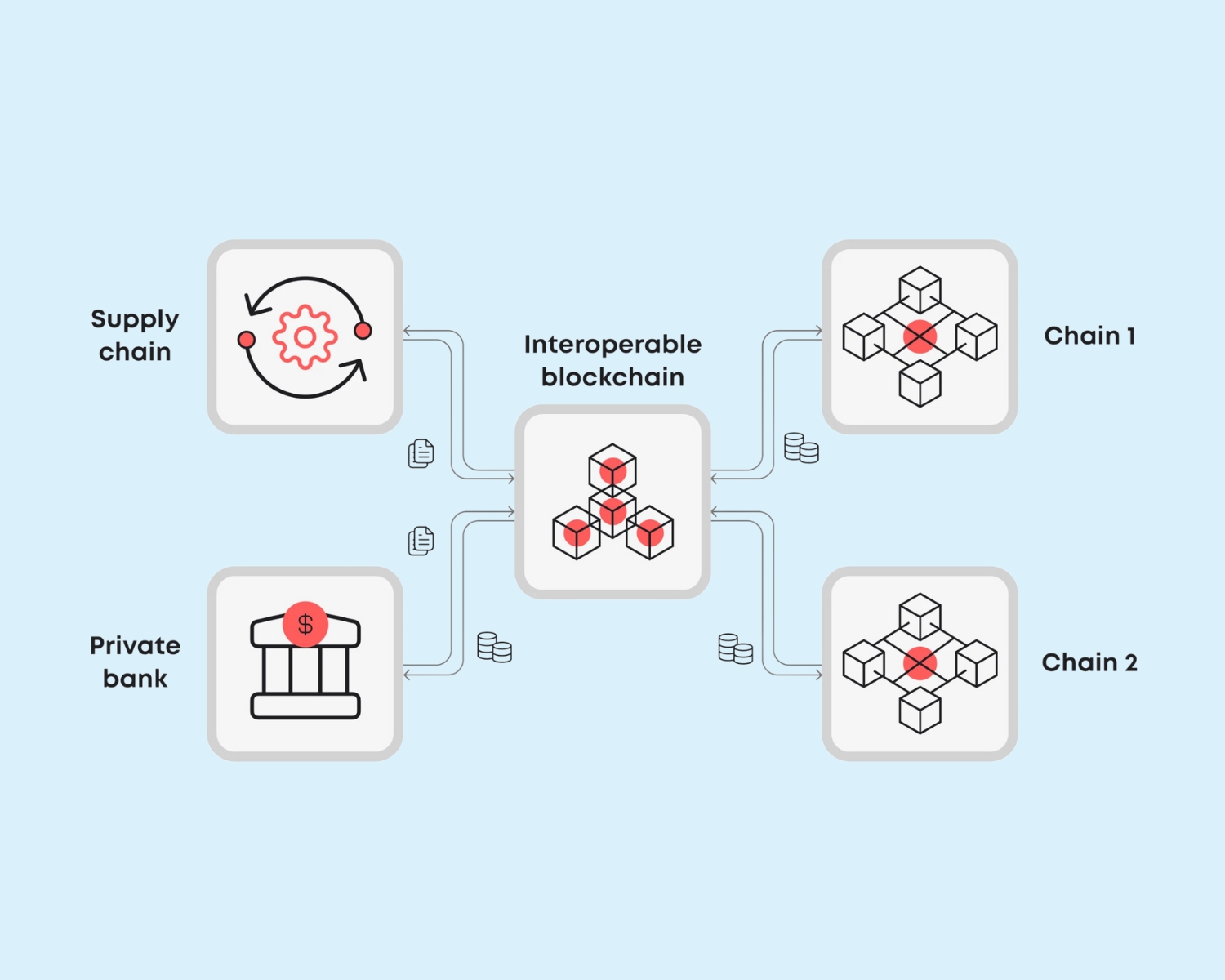
Introduction
As the blockchain ecosystem grows, different networks operate independently, creating fragmentation and inefficiencies in decentralized applications (dApps), finance (DeFi), and NFTs. The solution? Blockchain interoperability—the ability for different blockchains to communicate, share data, and transfer assets seamlessly.
With advancements in cross-chain solutions like Polkadot, Cosmos, and Layer 2 protocols, blockchain interoperability is becoming a reality, paving the way for a fully connected, decentralized world.
1. Why Blockchain Interoperability Matters
Currently, most blockchains are isolated, limiting their ability to share data and assets across networks. This creates problems such as:
● Lack of scalability: Transactions are confined to one blockchain, leading to congestion (e.g., Ethereum gas fees).
● Fragmented liquidity: Assets are siloed within specific chains, limiting DeFi adoption.
● User friction: Moving assets between blockchains requires third-party bridges, which can be slow and insecure.
Blockchain interoperability breaks down these barriers, allowing seamless network interaction and unlocking new use cases in DeFi, NFTs, and supply chain management.
2. Leading Cross-Chain Solutions Enabling Interoperability
Several projects are leading the charge to connect blockchains and enable seamless asset transfers:
a. Polkadot: The Multi-Chain Network
Polkadot is designed as a multi-chain ecosystem, connecting blockchains via its Relay Chain and enabling:
● Parachain communication: Blockchains can transfer data and assets securely.
● Cross-chain DeFi applications: Users can interact with dApps across different networks.
● Scalability improvements: Transactions are processed in parallel across parachains.
b. Cosmos: The Internet of Blockchains
Cosmos uses the Inter-Blockchain Communication (IBC) protocol, allowing independent blockchains to:
● Transfer tokens and assets across chains securely.
● Connect DeFi applications across different blockchain ecosystems.
● Reduce reliance on centralized exchanges for cross-chain transactions.
c. Layer 2 Solutions: Faster Transactions & Lower Fees
Layer 2 protocols like Polygon, Arbitrum, and Optimism enhance Ethereum’s scalability while enabling:
● Seamless asset transfers between Ethereum and Layer 2 chains.
● Lower gas fees and faster transactions for DeFi users.
● Interoperability between Ethereum-based dApps and other ecosystems.
3. The Future of Interoperable Blockchains
With these innovations, we are moving toward a genuinely interconnected blockchain world where:
● Users can move assets between chains without friction.
● DeFi protocols can tap into liquidity from multiple blockchains.
● Businesses can build decentralized applications (dApps) that work across various networks.
As blockchain adoption increases, interoperability will be the key to mass adoption, making decentralized applications more accessible, scalable, and efficient.
Conclusion
Blockchain interoperability is no longer a concept—it’s becoming a core feature of the decentralized web. With Polkadot, Cosmos, and Layer 2 protocols leading the charge, the future will see seamless cross-chain interactions, lower fees, and more significant innovation in DeFi, NFTs, and dApps.
Interoperability will be the foundation of the next wave of blockchain advancements as we move towards a fully connected, decentralized world.